Python & Machine Learning : Step-by-Step Guide
Machine Learning: The Future of Business. Its rapid advancements in recent years have propelled organizations to harness its potential for achieving tangible results and unlocking unprecedented levels of accuracy and insight.
Step 1. Install Python
#In case of windows Installation
- Download Python: Go to the official Python website (python.org) and download the latest version of Python for your operating system.
- Run the Installer: Locate the downloaded Python installer and run it. Follow the installation wizard's prompts to customize the installation if desired, or simply use the default settings.
- Add Python to PATH: During the installation process, you will have the option to add Python to the system PATH. Enable this option to easily run Python from the command line.
- Verify Installation: Open a command prompt or terminal and type "python" followed by Enter. If Python is installed correctly, you should see the Python version and the interactive Python shell (>>>).
#In case of Linux Installation
- Open a terminal: Launch the terminal application on your Linux system. You can usually find it in the Applications menu or use the shortcut Ctrl+Alt+T.
Update package lists: Run the following command to update the package lists and ensure you have the latest software information:
sudo apt update
Install Python: Run the following command to install Python:
sudo apt install python3
Verify the installation: After the installation is complete, you can verify it by checking the Python version. Run the following command:
python3 --version
You should see the version number displayed, confirming that Python is installed correctly.Install pip (optional): Pip is a package manager for Python that allows you to easily install additional libraries and packages. To install pip, run the following command:
sudo apt install python3-pipVerify pip installation: After the installation is complete, you can verify it by checking the pip version. Run the following command:
pip3 --version
You should see the version number displayed, confirming that pip is installed correctly. Now you have successfully installed Python on your Linux system and you're ready to start coding in Python.
Step 2: Creating a sample program Hello world
Open any text editor and create a new file sample.py. The python file always should have an extension of ".py" . In that file, type
print("Hello, World!")
Save that file and got to command prompt and type python hello.py Now the output will be
Hello, World!
Step 3: Installing IDE
We can use even Eclipse to run a Python or Machine Learning program by just including a plugin called "Pydev".
There are actually many IDEs for the development of the ML or Python project like Pycharm, IDLE, Anaconda etc.
For the Pycharm Installation on Windows,
Go to this link http://www.python.org/downloads/, and follow and install the steps. Choose Customise installation to install in a particular folder.
For the Pycharm Installation on Linux,
Go to this link https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/, and execute the below cmds in the command prompt
cd ~/Downloads
ls pycharm*
tar -xvzf pycharm-professional-2016.2.3.tar.gz -C ~
To run Pycharm, first navigate to your source folder
cd ~
ls
cd pycharm-2016.2.3/bin
sh pycharm.sh &
Step 4: Creating a simple Machine Learning program using Python
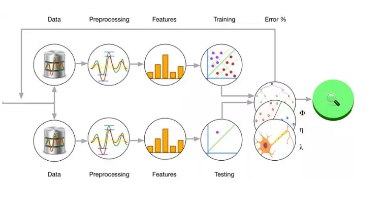
There are many packages in Machine Learning which helps in tasks like text classification, probability and sentimental analysis etc. For the text classification nltk (Natural Language Toolkit) is the most used library. For calculation or deep learning numpy, pandas, tensorflow etc are useful.
Now we see how to get the count of positive and negative words using Supervised Classification in Machine Learning. Here first we need to import the nltk package which is required for text classification. Then we are creating two lists for both positive and negative words.
After that we can pass whichever sentences are needed to test. Those sentences every time goes inside a loop where the length(count) has been calculated and sent to find the ratio of positive and negative words. The counts would be divided by the length of words and would be taken as the final ratio of the respective positive and negative words. The output would be in the ratio of 0.3333333333333333, 0.25 respectively.
<span class="kwd">from</span><span class="pln"> __future__ </span><span class="kwd">import
</span><span class="pln"> division
import nltk
neg_words </span><span class="pun">=</span> <span class="pun">[</span><span class="str">'poor'</span><span class="pun">,</span> <span class="str">'horrible', 'unpleasant', 'unwelcome'</span><span class="pun">]</span><span class="pln">
pos_words </span><span class="pun">=</span> <span class="pun">[</span><span class="str">'excellent'</span><span class="pun">,</span> <span class="str">'nice', 'outstanding', 'awesome'</span><span class="pun">]</span><span class="pln">
Sentences </span><span class="pun">=</span> <span class="pun">[</span><span class="str">"the picture is horrible and unpleasant"</span><span class="pun">,</span> <span class="str">"that was really nice"</span><span class="pun">]</span>
<span class="kwd">for</span><span class="pln"> element </span><span class="kwd">in</span><span class="pln"> Sentences</span><span class="pun">:</span>
<span class="com"># split the <span class="pln">element </span>into words:</span><span class="pln">
words </span><span class="pun">=</span><span class="pln"> element </span><span class="pun">.</span><span class="pln">split</span><span class="pun">()</span>
<span class="com"># create lists of positive and negative words </span>
<span class="com"># words in the current <span class="pln">element and finding the length of words</span> to get the counts in </span><span class="com">each list:</span><span class="pln">
count_pos </span><span class="pun">=</span><span class="pln"> len</span><span class="pun">([</span><span class="pln">w </span><span class="kwd">for</span><span class="pln"> w </span><span class="kwd">in</span><span class="pln"> words </span><span class="kwd">if</span><span class="pln"> w </span><span class="kwd">in</span><span class="pln"> pos_words</span><span class="pun">])</span><span class="pln">
count_neg </span><span class="pun">=</span><span class="pln"> len</span><span class="pun">([</span><span class="pln">w </span><span class="kwd">for</span><span class="pln"> w </span><span class="kwd">in</span><span class="pln"> words </span><span class="kwd">if</span><span class="pln"> w </span><span class="kwd">in</span><span class="pln"> neg_words</span><span class="pun">])</span>
<span class="com"># calculating the ratio by taking the count and the length of words:</span><span class="pln">
ratio_pos </span><span class="pun">=</span><span class="pln"> count_pos </span><span
class="pun">/</span><span class="pln"> len</span><span class="pun">(</span><span
class="pln">words</span><span class="pun">)</span><span class="pln">
ratio_neg </span><span class="pun">=</span><span class="pln"> count_neg </span><span
class="pun">/</span><span class="pln"> len</span><span class="pun">(</span><span
class="pln">words</span><span class="pun">)</span>
<span class="kwd">print</span><span class="pun">("ratio of positive words",</span><span
class="pln">ratio_pos</span><span class="pun">)</span>
<span class="kwd">print</span><span class="pun">("ratio of negative words",</span><span
class="pln">ratio_neg)
</span>